Glucose transporter-1 as an independent prognostic marker for cancer: a meta-analysis
Zheng-Xiao Zhao, Lin-Wei Lu, Jian Qiu, Qiu-Ping Li, Fei Xu, Bao-Jun Liu, Jing-Cheng Dong and Wei-Yi Gong*
Oncotarget, Advance Publications
Objective: Glucose transporter-1 (GLUT-1) as the major glucose transporter present in human cells is found overexpressed in a proportion of human malignancies. This meta-analysis is attempted to assess the prognostic significance of GLUT-1 for survival in various cancers.
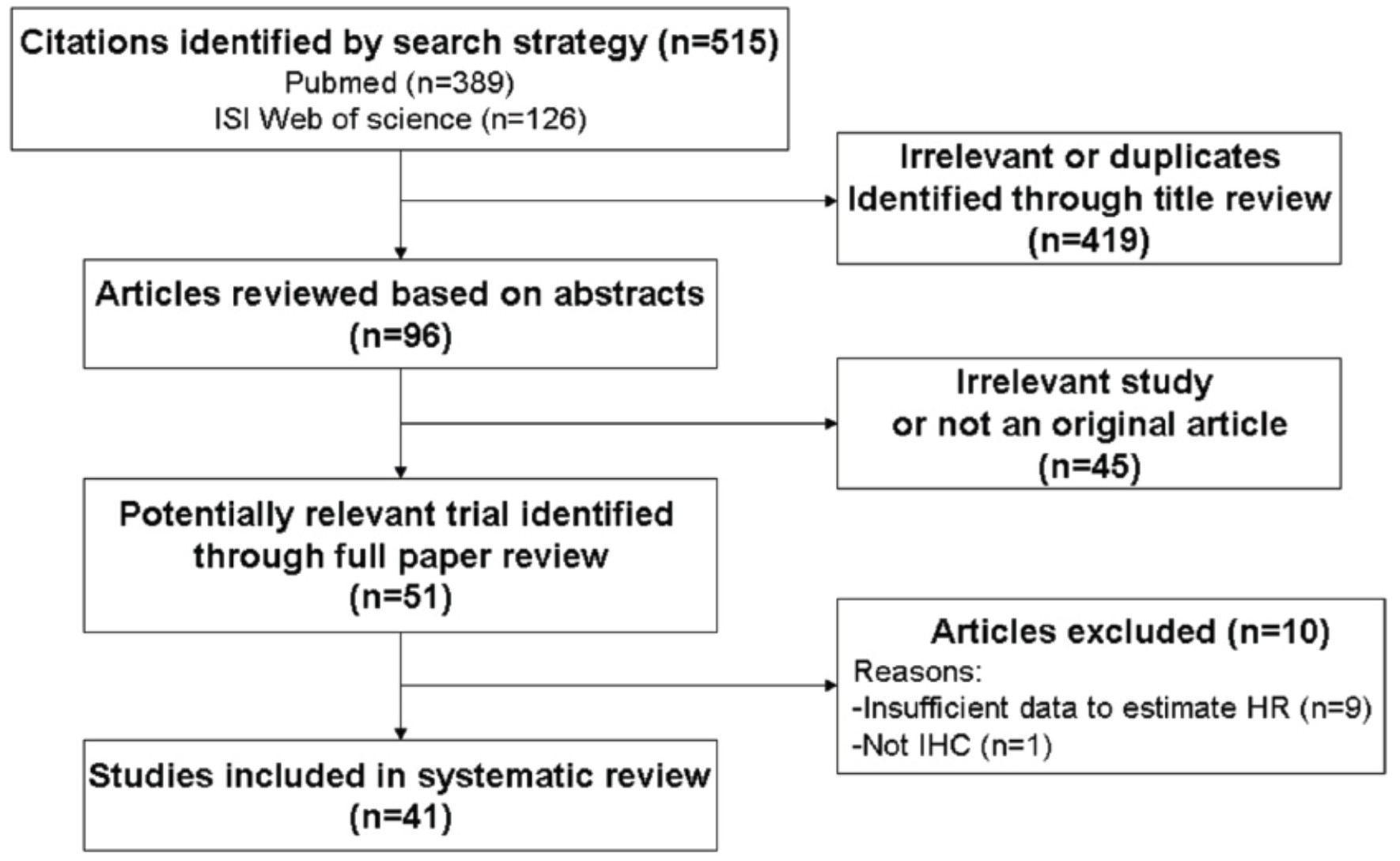
Materials and Methods: We conducted an electronic search using the databases PubMed, Embase and Web of Science, from inception to Oct 20th, 2016. Pooled hazardratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
Results: Fourty-one studies with a total of 4794 patients were included. High GLUT-1 expression was significantly associated with poorer prognosis [overall survival: HR = 1.833 (95% CI: 1.597–2.069, P < 0.0001); disease-free survival: HR = 1.838 (95% CI: 1.264–2.673, P < 0.0001); progression-free survival: HR = 2.451 (95% CI: 1.668–3.233, P < 0.0001); disease specific survival: HR = 1.96 (95% CI: 1.05–2.871, P < 0.0001)].
Conclusions: High GLUT-1 expression may be an independent prognostic marker to predict poor survival in various types of cancers. Further clinical trials with high quality need to be conducted to confirm our conclusion.