Cell Death and Differentiation: 发表中国乳腺癌研究重要成果

2017年10月13日,英国《自然》旗下《细胞死亡与分化》在线发表中国科技大学、复旦大学附属肿瘤医院、厦门大学、中国科学院、安徽省立医院、安徽医科大学第一附属医院、密歇根大学综合癌症中心、复旦大学上海医学院和生物医学研究院的研究报告,发现通过阻断白细胞介素6(IL6)可增强γ分泌酶抑制剂对Notch3受体阳性乳腺癌的抗肿瘤作用。
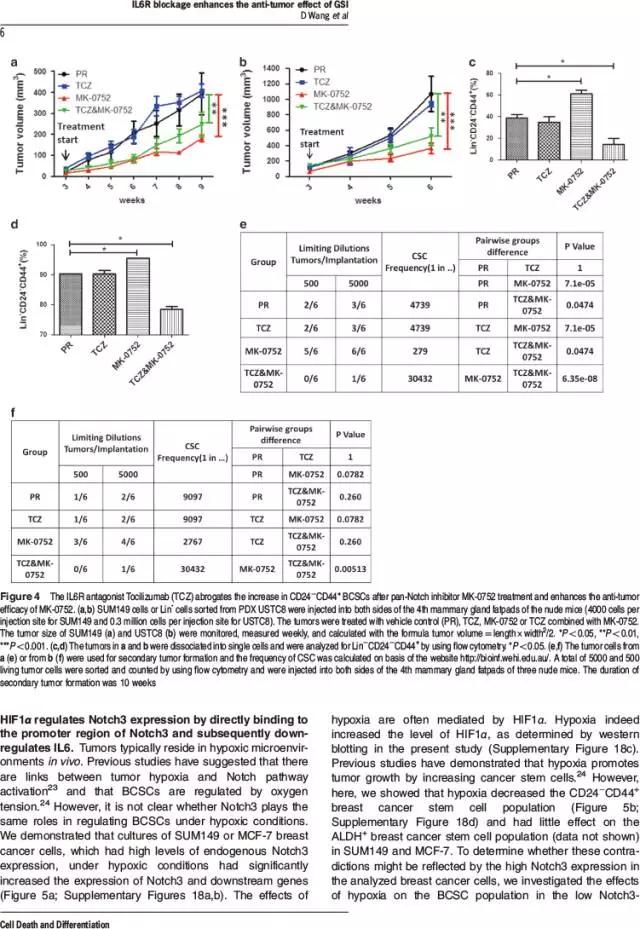
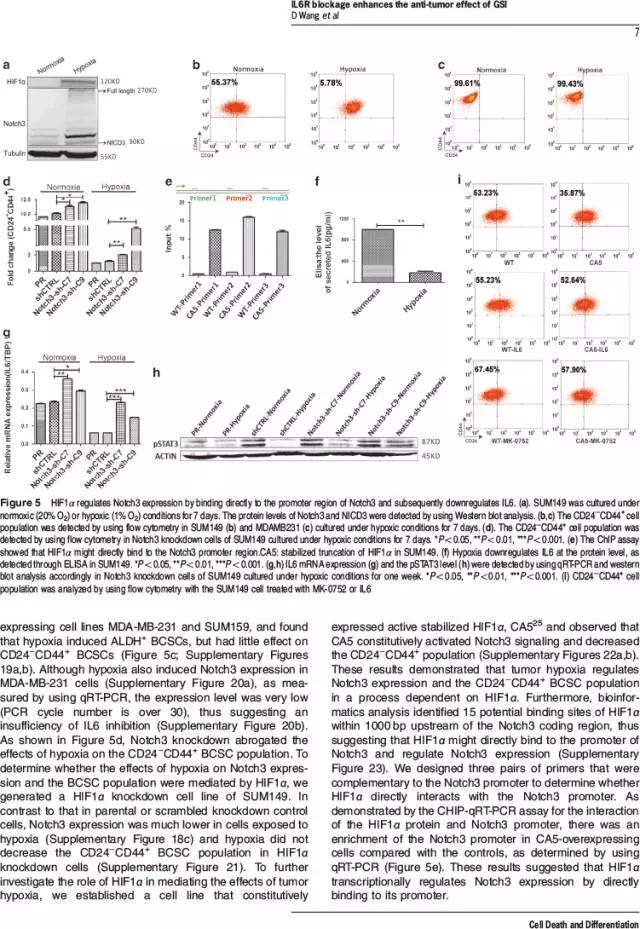
该研究证实γ分泌酶抑制剂(例如MK-0752和RO4929097)可以抑制乳腺肿瘤生长,但是也可增加Notch3受体阳性乳腺癌细胞的乳腺癌干细胞数量,该过程与IL6分泌协同进行,并且可被托珠单抗(IL6受体拮抗剂)阻断。MK-0752抑制Notch3-Hey2信号传导可以引起IL6分泌。此外,缺氧诱导因子1α(HIF1α)通过直接结合Notch3启动子,可以上调Notch3表达,并且通过降低Notch3受体阳性乳腺癌细胞的IL6水平,从而减少乳腺癌干细胞。
该研究利用乳腺癌细胞株异种移植物和患者来源异种移植物,发现MK-0752联合托珠单抗可以显著减少乳腺癌干细胞、抑制肿瘤生长,从而可以作为治疗Notch3受体阳性乳腺癌的新策略。
Cell Death Differ. 2017 Oct 13. [Epub ahead of print]
IL6 blockade potentiates the anti-tumor effects of γ-secretase inhibitors in Notch3-expressing breast cancer.
Dong Wang, Jiahui Xu, Bingjie Liu, Xueyan He, Lei Zhou, Xin Hu, Feng Qiao, Anli Zhang, Xiaojun Xu, Huafeng Zhang, Max S Wicha, Lixing Zhang, Zhi-ming Shao, Suling Liu.
University of Science & Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China; Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China; Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, China; Anhui Provincial Hospital, Hefei, Anhui, China; The First Affiliated Hospital, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China; University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center, Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China; Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
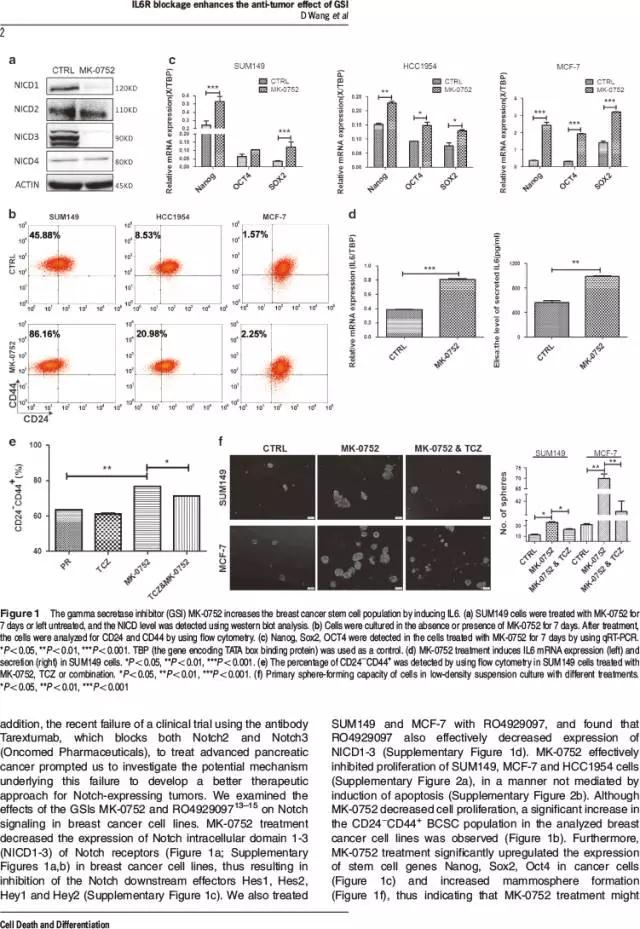
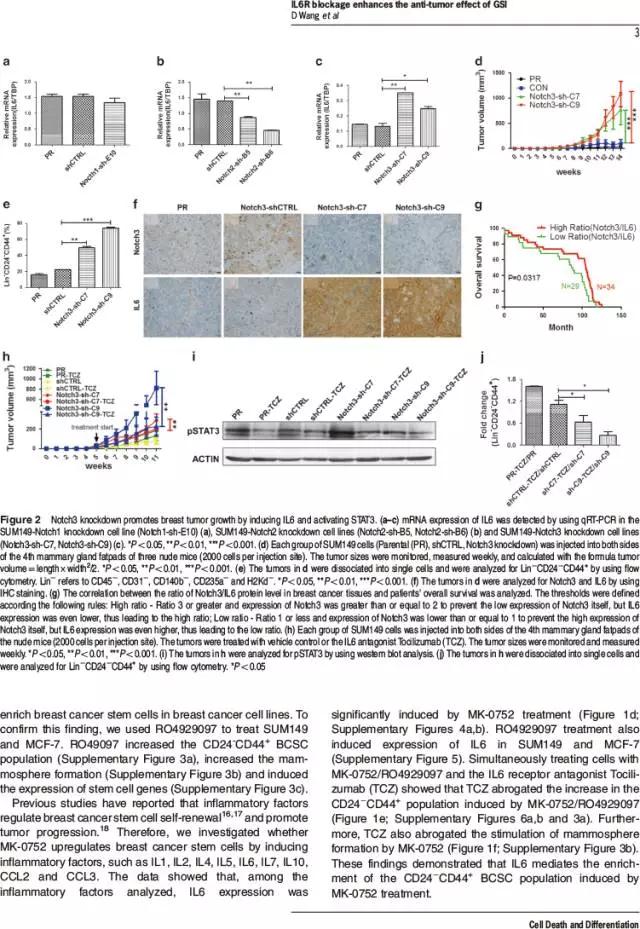
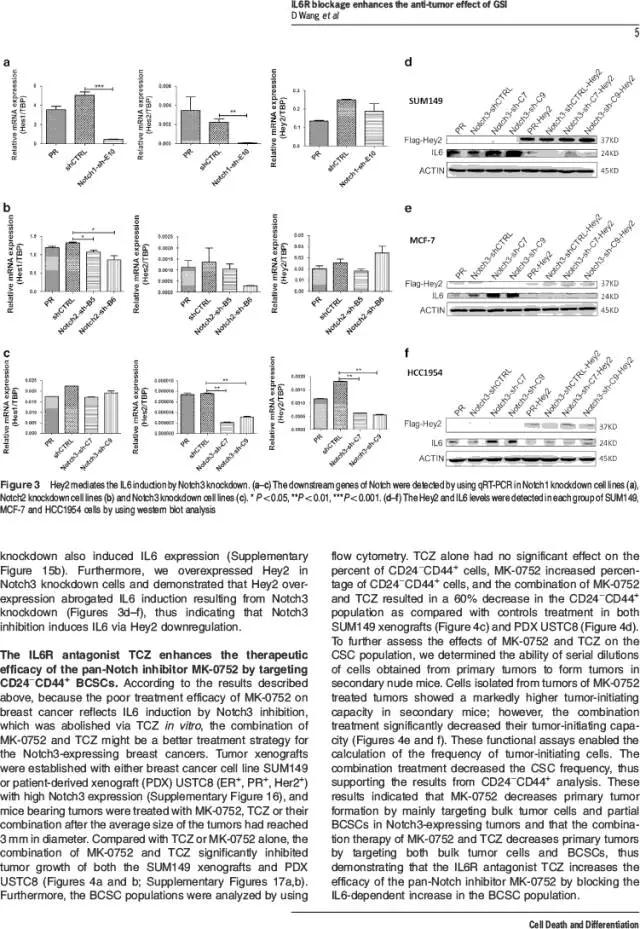
Notch pathways have important roles in carcinogenesis including pathways involving the Notch1 and Notch2 oncogenes. Pan-Notch inhibitors, such as gamma secretase inhibitors (GSIs), have been used in the clinical trials, but the outcomes of these trials have been insufficient and have yielded unclear. In the present study, we demonstrated that GSIs, such as MK-0752 and RO4929097, inhibit breast tumor growth, but increase the breast cancer stem cell (BCSC) population in Notch3-expressing breast cancer cells, in a process that is coupled with IL6 induction and is blocked by the IL6R antagonist Tocilizumab (TCZ). IL6 induction results from inhibition of Notch3-Hey2 signaling through MK-0752. Furthermore, HIF1α upregulates Notch3 expression via direct binding to the Notch3 promoter and subsequently downregulates BCSCs by decreasing the IL6 levels in Notch3-expressing breast cancer cells. Utilizing both breast cancer cell line xenografts and patient-derived xenografts (PDX), we showed that the combination of MK-0752 and Tocilizumab significantly decreases BCSCs and inhibits tumor growth and thus might serve as a novel therapeutic strategy for treating women with Notch3-expressing breast cancers.





From 细胞死亡与分化


